一、背景与现状
目前,我们团队在使用 Kafka 时主要存在以下几类问题:
- 问题一:一个工程对接多套 Kafka 集群,工程代码缺少对多套集群的规范管理;
- 问题二:生产环境分为基线和灰度,对接灰度 Kafka 时,工程改动繁琐;
- 问题三:生产/消费消息时,出现大量偏技术性的重复代码:序列化、反序列化、判空、重试等;
- 问题四:在发送消息、消费消息过程中,存在链路丢标的情况;
因此,建设统一消息组件,以解决上述问题,简化消息收发。
1.1 发送消息现状
生产环境有两套:生产基线环境和生产灰度环境。
1、基线生产者
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| @Service
public class KafkaProducerServiceImpl {
@Value("${kafka.servers}")
private String kafkaServers;
private Producer<String, String> producer;
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
Properties props = new Properties();
props.put("bootstrap.servers", kafkaServers);
props.put("acks", "all");
props.put("key.serializer", "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer");
props.put("value.serializer", "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer");
props.put("retries", 0);
props.put("linger.ms", 5);
props.put("batch.size", 16384);
props.put("buffer.memory", 33554432);
producer = new KafkaProducer<>(props);
}
public void sendMessage(String topic, String key, String value) {
ProducerRecord<String,String> producerRecord = new ProducerRecord<>(topic, null, key, value, null);
Future<RecordMetadata> sendFuture = producer.send(producerRecord);
sendFuture.get();
}
}
|
2、灰度生产者
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| public class GrayKafkaProducerServiceImpl {
@Value("${gray.kafka.servers}")
private String grayKafkaServers;
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
Properties props = new Properties();
props.put("bootstrap.servers", grayKafkaServers);
}
}
|
3、发送消息
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| public void send(Message message) {
String value = JSON.toJSONString(message);
if (GrayUtils.isGray()) {
grayKafkaProducerService.sendMessage("order.topic", message.getOrderId(), value);
} else {
kafkaProducerServiceImpl.sendMessage("order.topic", message.getOrderId(), value);
}
}
|
2.2 消费消息现状
1、配置消费者
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| @Configuration
@EnableKafka
public class ConsumerConfig {
@Value("${kafka.servers}")
private String kafkaServers;
@Value("${gray.kafka.servers}")
private String grayKafkaServers;
@Bean
public DefaultKafkaConsumerFactory<String, String> consumerFactory() {
HashMap<String, Object> configs = new HashMap<>();
configs.put(ConsumerConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG, kafkaServers);
configs.put(ConsumerConfig.GROUP_ID_CONFIG,"example-consumer-group");
configs.put(ConsumerConfig.ENABLE_AUTO_COMMIT_CONFIG, false);
configs.put(ConsumerConfig.KEY_DESERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG,"org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializer");
configs.put(ConsumerConfig.VALUE_DESERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG,"org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializer");
configs.put(ConsumerConfig.MAX_POLL_INTERVAL_MS_CONFIG, 480000);
configs.put(ConsumerConfig.MAX_POLL_RECORDS_CONFIG, 30);
return new DefaultKafkaConsumerFactory<>(configs);
}
@Bean
public DefaultKafkaConsumerFactory<String,String> grayConsumerFactory() {
}
}
|
2、注册监听
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| @Bean
public ConcurrentMessageListenerContainer concurrentMessageListenerContainer(MessageListener exampleMessageListener) {
ContainerProperties containerProperties = new ContainerProperties("order.topic");
containerProperties.setMessageListener(exampleMessageListener);
ConcurrentMessageListenerContainer<String, String> listenerContainer = new ConcurrentMessageListenerContainer<>(
GrayUtils.isGray() ? grayConsumerFactory() : consumerFactory(),
containerProperties);
listenerContainer.setConcurrency(15);
return listenerContainer;
}
|
3、逻辑处理
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| @Service
public class ExampleMessageListener extends MessageListener<String, String> {
@Override
public void onMessage(ConsumerRecord<String, String> record) {
Message message = JSON.parseObject(record.value(), Message.class);
try {
doProcess(message);
} catch (CustomException e) {
log.error(e.getMessage, e);
} catch (Throwable ex) {
doRetry(message);
}
}
}
|
二、EasyKafka - 快速开始
EasyKafka 是基于 Spring Kafka 的增强,原 Spring Kafka 所有功能完全适配。
EasyKafka 的建设目标:使消息的发送和接收更简单。项目地址:https://github.com/studeyang/easykafka
主要解决以下问题:
- 简化消息发送和接收流程
- 封装基线与灰度环境兼容的复杂度
- 统一消息重试
2.1 发送消息
1、引入依赖
1
2
3
4
| <dependency>
<groupId>io.github.studeyang</groupId>
<artifactId>easykafka-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
|
2、配置
最少启动配置
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| easykafka:
init:
kafkaCluster:
- cluster: send
brokers: send-kafka.domain.com:9092
- cluster: send
brokers: send-gray-kafka.domain.com:9092
tag: gray
- cluster: edms
brokers: edms-kafka.domain.com:9092
|
3、定义一条消息
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| import io.github.open.easykafka.client.annotation.Topic;
import io.github.open.easykafka.client.message.Event;
@Topic(cluster = "send", name = "easykafka-example-topic")
public class ExampleEvent extends Event {
private String name;
}
|
4、发送消息
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| import io.github.open.easykafka.client.EventPublisher;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class EventPublisherTest {
@Test
public void sendExampleEvent() {
ExampleEvent event = new ExampleEvent();
event.setName("test");
EventPublisher.publish(event);
}
}
|
2.2 消费消息
1、引入依赖
引入 EasyKafka 和 消息定义包的依赖。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
<dependency>
<groupId>io.github.studeyang</groupId>
<artifactId>easykafka-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.github.studeyang</groupId>
<artifactId>es-send-basic-api</artifactId>
</dependency>
|
2、实现消费逻辑
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| import io.github.open.easykafka.client.annotation.EventHandler;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class SingleEventHandler {
@EventHandler
public void handle(ExampleEvent event) {
System.out.println("收到了一条消息: " + event);
}
}
|
三、EasyKafka - 进阶使用
3.1 统一配置
1、初始化配置
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| easykafka:
init:
kafkaCluster:
- cluster: send
brokers: send-kafka.domain.com:9092
tag: BASE
- cluster: send
brokers: send-gray-kafka.domain.com:9092
tag: GRAY
- cluster: edms
brokers: edms-kafka.domain.com:9092
producer:
- beanName: sendProducer
config:
acks: 1
linger.ms: 10
- beanName: sendGrayProducer
config:
consumer:
- beanName: sendConsumer
config:
enable.auto.commit: false
max.poll.records: 50
- beanName: sendGrayConsumer
config:
|
2、运行时配置
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| easykafka:
runtime:
producer:
partitionSize: 500
async:
corePoolSize: 3
maxPoolSize: 5
keepAliveSeconds: 60
queueCapacity: 100
rejectedHandler: java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy
threadNamePrefix: kafka-async-producer-
|
3.2 生产者
1、初始化Kafka
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| easykafka:
init:
kafkaCluster:
- cluster: send
brokers: send-kafka.domain.com:9092
tag: base
- cluster: send
brokers: send-gray-kafka.domain.com:9092
tag: gray
- cluster: edms
brokers: edms-kafka.domain.com:9092
tag: base
|
当初始化 Kafka 配置如上时,程序启动后会产生一个生产者容器 ProducerContainer。
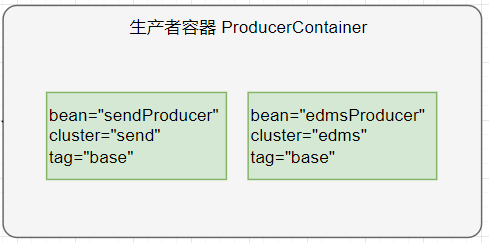
容器内容通过日志打印出来,如下:
1
2
3
| [EasyKafka] ProducerContainer:
{"bean":"postGrayProducer","cluster":"post","tag":"BASE"}
{"bean":"edmsGrayProducer","cluster":"edms","tag":"BASE"}
|
如果当前运行的是灰度环境(ENV_TAG=gray),容器包含内容如下::
1
2
3
| [EasyKafka] ProducerContainer:
{"bean":"postGrayProducer","cluster":"post","tag":"GRAY"}
{"bean":"edmsGrayProducer","cluster":"edms","tag":"GRAY"}
|
2、消息发送流程
定义好消息后:
1
2
3
4
| @Topic(cluster = "send", name = "easykafka-example-topic")
public class ExampleEvent extends Event {
private String name;
}
|
消息发送时,会根据消息定义的 @Topic(cluster) 值,从生产者容器 ProducerContainer 选择合适的 Producer 发送消息。
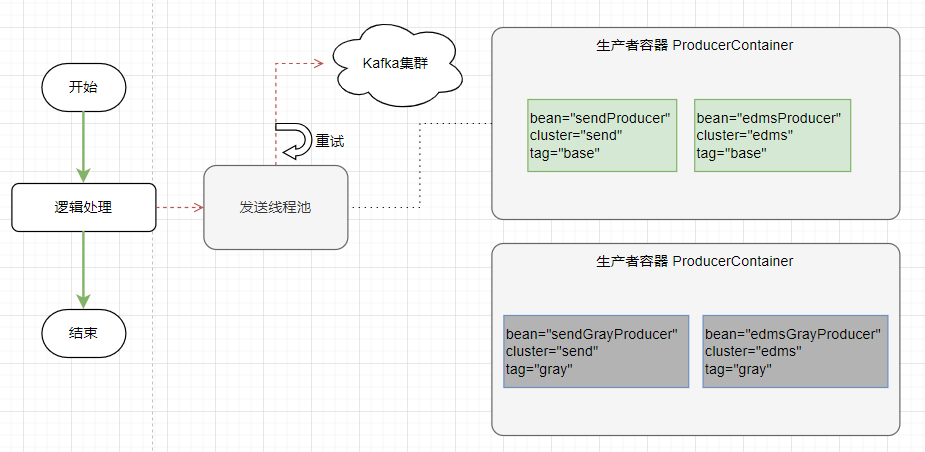
如果当前运行的是灰度环境(ENV_TAG=gray),在程序启动后,生产者容器内容也会发生相应的变化。
3、扩展 producer 配置
例如我想改 producer 的配置,acks=1; linger.ms=10,可以通过 config 来扩展或覆盖配置。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| easykafka:
init:
producer:
- beanName: sendProducer
config:
acks: 1
linger.ms: 10
- beanName: sendGrayProducer
config:
|
4、使用原生 producer
也可以用原生的 kafka producer 发送消息,但这种方式不推荐使用。
1
2
3
4
5
6
| @Service
public class DemoServiceImpl {
@Autowired
@Qualifier("sendProducer")
private Producer<String, String> sendProducer;
}
|
3.3 消费者
1、初始化监听器
EasyKafka 会扫描 @EventHandler 注解,以获得所有的监听器。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| @Service
public class SingleEventHandler {
@EventHandler
public void handle(ExampleEvent event) {
System.out.println("SingleEventHandler 收到消息: " + event);
}
@EventHandler(concurrency = "15", groupId = "groupId-example-consumer")
public void handle(Example2Event event) {
System.out.println("SingleEventHandler 收到消息: " + event);
}
}
|
@EventHandler 的默认配置:
- cluster 默认从
ExampleEvent 的 @Topic 注解中获取
- topics 默认从
ExampleEvent 的 @Topic 注解中获取
- groupId 默认取
spring.application.name
- containerFactory 默认取
{cluster} + "KafkaListenerContainerFactory"
所有的监听器都会放到监听器容器 ListenerContainer 中。在代码扫描后,监听器容器中的内容通过控制台日志打印,如下:
1
2
3
| [EasyKafka] ListenerContainer:
{"cluster":"send","event":"io.github.open.easykafka.event.ExampleEvent","groupId":"example-consumer","topics":"easykafka-example-topic"}
{"cluster":"send","event":"io.github.open.easykafka.event.Example2Event","groupId":"groupId-example-consumer","topics":"easykafka-example-topic"}
|
2、消息消费流程
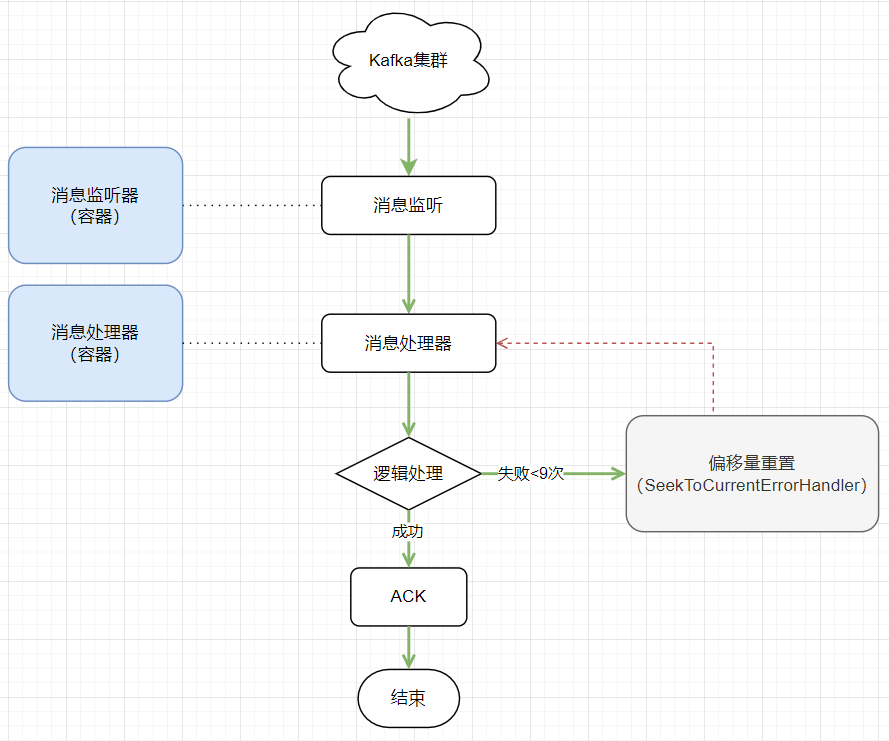
消息一旦消费失败,会使用 Spring Kafka 的默认错误处理 SeekToCurrentErrorHandler 进行消息重试,最大重试次数= 9 次。
3、扩展 consumer 配置
例如我想改 consumer 的配置,enable.auto.commit=false; max.poll.records=50,可以通过 config 来扩展或覆盖配置。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| easykafka:
init:
consumer:
- beanName: sendConsumer
config:
enable.auto.commit: false
max.poll.records: 50
- beanName: sendGrayConsumer
config:
|
也可以使用 @EventHandler 的 properties 属性来配置,该属性与 @KafkaListener 的 properties 用法和功能完全一样,例如:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| @Service
public class SingleEventHandler {
@EventHandler(properties = {"enable.auto.commit=false", "max.poll.records=50"})
public void handle(ExampleEvent event) {
System.out.println("SingleEventHandler 收到消息: " + event);
}
}
|

封面
相关文章






